Introduction
History of Database System
-
Manual Model
-
File System
Drawbacks of using file systems to store data:
- Data redundancy and inconsistency
- Difficulty in accessing data
- Data isolation
- Integrity problems
- Atomicity of updates
- Concurrent access by multiple users
- Security problems
-
Databse
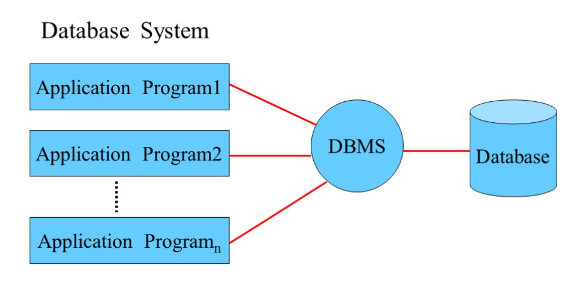
Benefits of database approach:
- Data can be shared
- Redundancy can be reduced
- Inconsistency can be avoided
- Transaction support can be provided
- Integrity can be maintained
- Security can be enforced
- ...
What is Database Systems
DB: database, a collection of interrelated data
DBMS: Database Management System
Application: Set of programs to access the data
DBMS contains information about:
- Collection of interrelated data
- Set of programs to access the data
- An environment that is both convenient and efficient to use
Three Levels and Data Abstraction
-
Physical level:
Describes how a record is physically stored.
-
Logical level:
Describes logical data stored in database and relationships among the data.
-
View level
Part of the entire database. Application programs hide details of data types. Views can also hide information for security purpose.
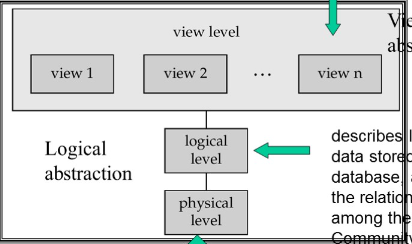
There are two mappings between three levels:
- The physical (internal) / logical (conceptual) mapping
- The view (external) /logical (conceptual) mapping
And database has two kinds of data independence:
-
Physical data independence
The ability to modify the physical schema without changing the logical schema or the views. So the application programs need not to be rewritten if the physical schema changes.
-
Logical data independence
The ability to modify the logical schema without changing the logical views.
Schema: the description of the structure of the data in a database.
Instance: the actual content of the database at a particular point in time.
Data Models: A collection of conceptual tools for describing data, data relationships, data semantics and consistency constrains.
- Data structure
- Data operations
- Constraint rules.
Database Languages
DDL: Data definition language, specification notation for definition the database schema.
DML: Data manipulation language: language for accessing the manipulating the data organized by the appropriate data model. For example: query, insert, delete and update. SQL is the most widely used query language.
Database Users
Users are differentiated by the way they expect to interact with the system.
- End users
- Application programmers
- Database analyzer and designer
- Database administrators(
DBA) - Database management system designer and implementer
Database System Structure
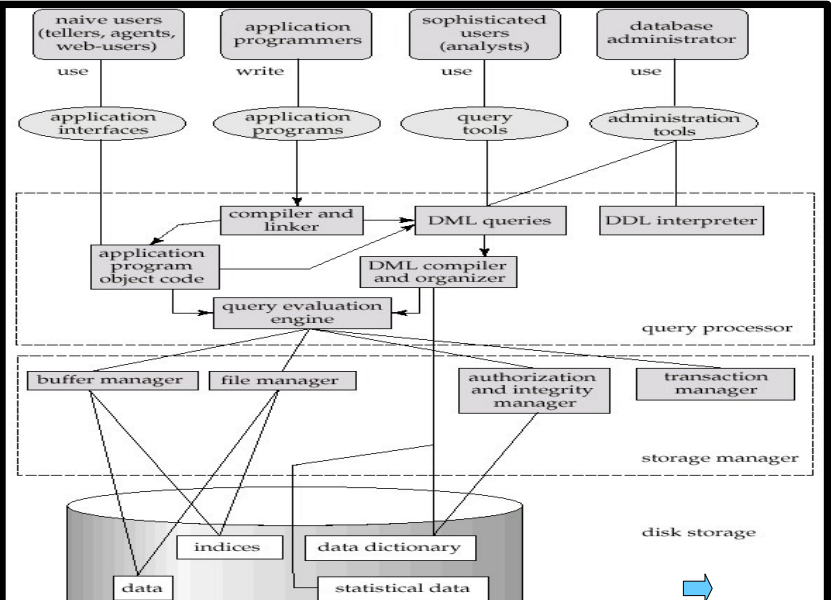
Storage Manager
Storage Management is a program module that provides the interface between the low level data stored in the database and the application programs and queries submitted to the system.
Query Processor
- DDL interpreter
- DML compiler
- Query optimization
- Query evaluation engine
Transaction Management
A transaction is a collection of operations that performs a single logical function in a database application.
Transaction management component ensures that the database remains in a consistent state. Concurrency-control manager controls the interaction among the concurrent transactions, to ensure the consistency of the database.